- Home
- Complications
- Insulin Resistance
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance can present with nonspecific symptoms such as fatigue, hypoglycemia, excess weight, high blood pressure, and high glucose and insulin levels.
However, these symptoms do not necessarily indicate insulin resistance, and most people may have it without realizing it.
Recognizing these symptoms alongside risk factors such as being overweight, belonging to a high-risk population, having a family history of type 2 diabetes, and having a large waist size can help with early intervention and prevention of type 2 diabetes.
In the following paragraphs, we will explain in details the symptoms of insulin resistance and importance of recognizing them in time.
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is an unusual condition in which cells in the body become less responsive to the hormone insulin. This means that the pancreas, which produces insulin, functions normally.
However, the body's cells do not respond adequately to insulin's effects. This will result in elevated levels of glucose in the bloodstream.
Unfortunately, this can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes and other health complications.
What are the
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance?
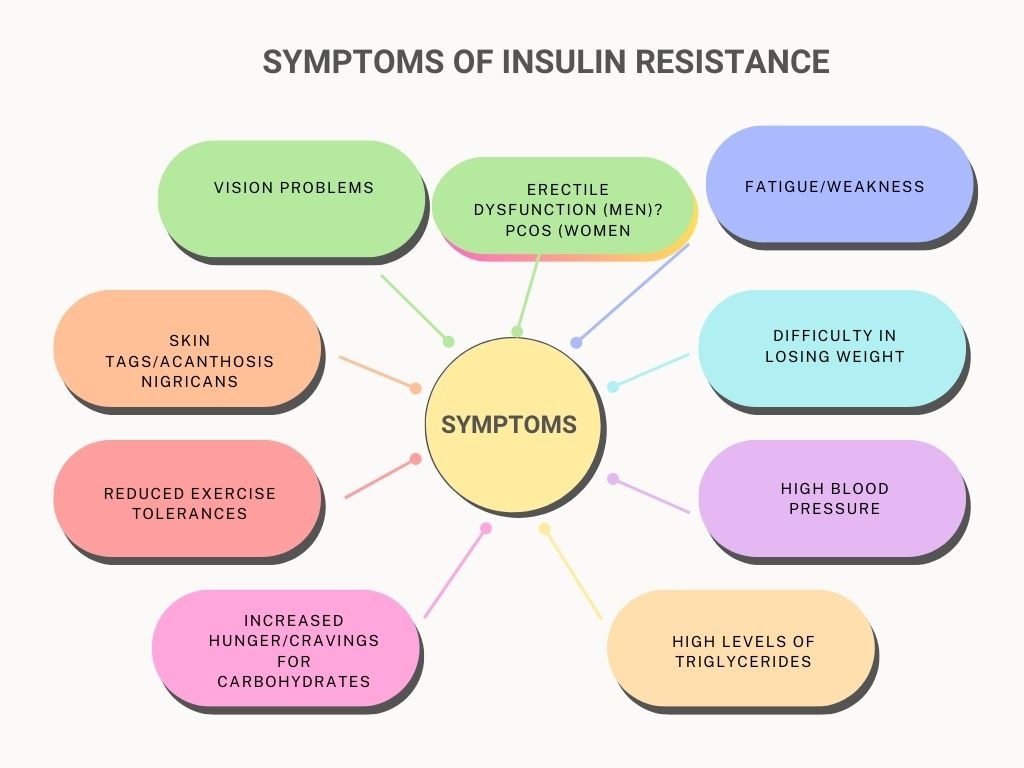
Insulin resistance typically develops slowly and may not produce any noticeable symptoms in the early stages.
As the condition progresses, however, several signs and symptoms may begin to emerge. These can include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Difficulty losing weight, especially in the midsection
- High blood pressure
- High levels of triglycerides and/or low levels of HDL cholesterol
- Increased hunger and cravings for carbohydrates
- Reduced tolerance for exercise
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women
- Skin tags, dark patches of skin, or acanthosis nigricans
- Erectile dysfunction in men
- Vision problems
It's important to note that many of these symptoms are also common in other conditions, so it's important to see a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Additionally, early intervention and treatment can help prevent or manage the long-term complications of insulin resistance, such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
How to recognize the
Symptoms of insulin resistance?
The symptoms of insulin resistance can be subtle and easy to miss, but early recognition is key.
Look out for signs such as fatigue, difficulty losing weight, high blood pressure, and increased hunger or cravings. If they do persist and are getting worse, should see your healthcare provider for further tests.
Seeing a healthcare professional for regular check-ups and blood tests can also help detect insulin resistance early.
If insulin resistance symptoms go unnoticed, it can lead to the development of type 2 diabetes.
However, recognizing the symptoms of insulin resistance in time can prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes in the future.
How far can I prevent future diabetes onset?
If you have symptoms of insulin resistance, early intervention through lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Managing other risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and obesity can also help reduce the risk of developing diabetes.
However, it's important to seek medical advice and monitoring from a healthcare professional to manage insulin resistance effectively and reduce the risk of future health complications.
It's essential to note that insulin resistance often presents with nonspecific symptoms, and many individuals may have it without realizing it.
These symptoms include fatigue, hypoglycemia, excess weight, high blood pressure, and high glucose and insulin levels.
These symptoms, however, do not necessarily indicate insulin resistance.
If you notice these symptoms alongside risk factors such as being overweight, over 40 years old, belonging to a high-risk population, having a family history of type 2 diabetes or other health conditions, and having a large waist size, early intervention can help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes.
|
Written by Dr.Albana Greca Sejdini, Md, MMedSc Medically reviewed by Dr.Ruden Cakoni, MD, Endocrinologist |
Last reviewed 04/11/2023 |
References:
References:
- Kahn, C. R. (2021). Insulin Resistance, Type 2 Diabetes, and Their Complications: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Treatment. In Williams Textbook of Endocrinology (14th ed., pp. 1446-1479). Elsevier.
- American Diabetes Association. (2018). Insulin resistance and prediabetes.
- Mayo Clinic. (2021). Insulin resistance. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/insulin-resistance/symptoms-causes/syc-20351899
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2021). Insulin resistance and prediabetes. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/prediabetes-insulin-resistance
Diabetes complications Questions or Problems? Get Help Here
This is the place where you can ask a question about any aspect of diabetes complications.
It's free and it's easy to do. Just fill in the form below, then click on "Submit Your Question".