- Home
- Natural Remedies
- A Simple Bitter Melon Diabetes Recipe
Bitter Melon for Diabetes
General Considerations

Here I’m trying to discuss what can bitter melon do to help you beat diabetes through realistic scientific researches as for other natural cures for diabetes.
Another name for bitter melon is the scientific name of Momordica charantia. However, it comes also with other names like: Bitter Gourd and Karela.
It grows in tropical areas such as: Asia, Africa, South America and Caribbean. People of these regions have always used bitter melon for various purposes.
In the Philippines, bitter melon tea is used for controlling blood sugar levels and diabetes, especially among the poor.
Ayurvedic is the Indian system of medicine. Since 1000 BC until today, it has been always focused on mind, body and spirit rather than the body alone in the treatment of all kinds of disease.
Thus, for treating diabetes and its complications, they include bitter melon and considered it as plant insulin.
Does Bitter Melon help lower blood sugar?
Certainly! Bitter melon is known for its ability to blood sugar levels. Bitter melon contains compounds like charantin, vicine and polypeptide p that are thought to have properties that can help in reducing blood sugar.
A number of studies have been conducted to explore the impact of melon on blood sugar levels.
Some research suggests that bitter melon may improve insulin sensitivity and reduce glucose absorption in the intestines.
However it's important to note that findings from these studies have been inconclusive and more research is required to establish the effectiveness of melon for diabetes management.
Is bitter melon effective for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
The potential effectiveness of bitter melon in managing diabetes may vary between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and it's important to understand the distinctions between the two conditions.
- Type 2 Diabetes:
Bitter melon has been traditionally used in some cultures as a remedy for managing blood sugar levels, and certain studies suggest it may have some benefits for individuals with type 2 diabetes.
Some research has indicated that bitter melon may help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetes.
However, results from studies are not always consistent, and more research is needed to establish the efficacy, optimal dosage, and long-term effects.
- Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by the immune system attacking and destroying the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. It typically requires insulin therapy.
Bitter melon's potential benefits in type 1 diabetes may be limited, as it primarily focuses on improving insulin sensitivity, and type 1 diabetes is characterized by a lack of insulin production.
Individuals with type 1 diabetes should not consider bitter melon or any other supplement as a substitute for insulin or other prescribed medications.
Instead, can use for other beneficial effects as antioxidants, etc. to protect body organs and prevent complications onset.
What are the active compounds in bitter melon that may contribute to its antidiabetic properties?
Bitter melon contains various bioactive compounds that might contribute to it anti-diabetic effect, including:
1. Charantin: The first component is called charantin, which consists of several natural steroids which have been shown to have blood glucose-lowering effects.
Charantin is believed to increase glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis in cells. It has been shown more effective than tolbutamide in lowering high blood sugar levels in some clinical studies.
2. Vicine and Polypeptide-p: These are proteins found in bitter melon fruit, seeds and tissue. They have been reported to have insulin-like effects, helping to lower blood sugar levels.
Researchers have found it very effective when administered subcutaneously, for both type 1 and 2 diabetics. This peptide is very similar to insulin, and can act like insulin.
3. Oleanolic acid glucosides : They are found in the fruit juice of bitter melon. I has shown good effects in improving blood sugar tolerance in type 2 diabetics.
4. Lectins: Bitter melon contains lectins, which are proteins that can bind to carbohydrates. Some lectins in bitter melon may have glucose-lowering effects.
5. Momordicosides: These are a group of triterpenoid compounds found in bitter melon. They have been investigated for their potential antidiabetic effects.
6. Cucurbitane-type triterpenoids: Bitter melon contains various triterpenoids that may contribute to its pharmacological activities, including potential effects on glucose metabolism.
7. Quercetin: Bitter melon is a good source of flavonoids, including quercetin, which has antioxidant properties and may have some impact on glucose metabolism.
They are 2 ways the bitter melon components act to lower blood sugar levels:
1. In case you have type 2 diabetes, your body can still produce insulin, but cannot use it properly.
Bitter melon tries not to accumulate too much sugar in your blood stream and helps your body cells to use it correctly.
2. The second way is by increasing the insulin production, thus lowering blood glucose.
What else can bitter melon do for your diabetes?
The bitter gourd components altogether can help lowering your high blood sugar levels, leading to a well – controlled diabetes, avoiding the onset of diabetes complications.
They can intensify the insulin production from the pancreas, due to the raise in beta cells (responsible for insulin production).
An additional positive effect of bitter melon is the lowering of total cholesterol.
Due to its anti-oxidant activity, it protects your kidneys and other organs from damages. This is achievee by the action of other components you may find in bitter gourd, such as zinc, vitamin B-complex, vitamin C, and poly-unsaturated fatty acids.
They all have anti-oxidant activity and as a consequence protects your kidneys and other organs from damages. Overall it can prevent diabetes complications onset.
In addition, it stimulates the amino acids uptake into muscles, and gives great improvements to your energy levels and your appetite.
Bitter melon is rich in iron, very important to your health.
And it contains some components that have good impact on AIDS virus and psoriasis and those with autoimmune diseases too.
Bitter melon can also favorably impact the aging process.
How should bitter melon be prepared and consumed for diabetes management?
Please take note that its flavor is very bitter, especially for the ripe fruit, but you can try various types of cooking it.
Drinking bitter melon juice in an empty stomach has shown to have better benefits in lowering high sugar levels.
Following are some common ways bitter melon can be prepared and consumed for potential diabetes management:
1. Fresh Bitter Melon: Wash the bitter melon thoroughly. Cut it lengthwise, and scoop out the seeds and pulp.
Slice or chop the melon into small pieces. You can eat it raw in salads or juice it. Keep in mind that the bitterness can be intense.
2. Bitter Melon Juice: Follow the steps for preparing fresh bitter melon. Use a juicer or blender to extract the juice. You may mix it with other vegetables or fruits to improve the taste.
3. Bitter Melon Tea: Dry bitter melon slices or use bitter melon tea bags, which are available in some health food stores.
Steep the slices or tea bags in hot water for about 10 minutes. Strain the tea and drink it. You can add honey or lemon for taste.
4. Cooked Bitter Melon: Stir-fry bitter melon with other vegetables and spices. This can help reduce the bitterness. Chinese mostly use it as an ingredient in stir fries, soups and teas.
While, in Pakistan and India, it’s prepared with potatoes and served with yogurt. Or they sparkle it with spices and fry in oil.
You can also stuff bitter melon with a mixture of ground meat, spices, and herbs, then cook it.
Meanwhile, in the Philippines, they know melon as ampalaya and serve it in several dishes. Also, they use shoots and leaves for salad greens.
5. Supplements: Bitter melon supplements, in the form of capsules or tablets, are also available.
However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as they can interact with medications or have side effects.
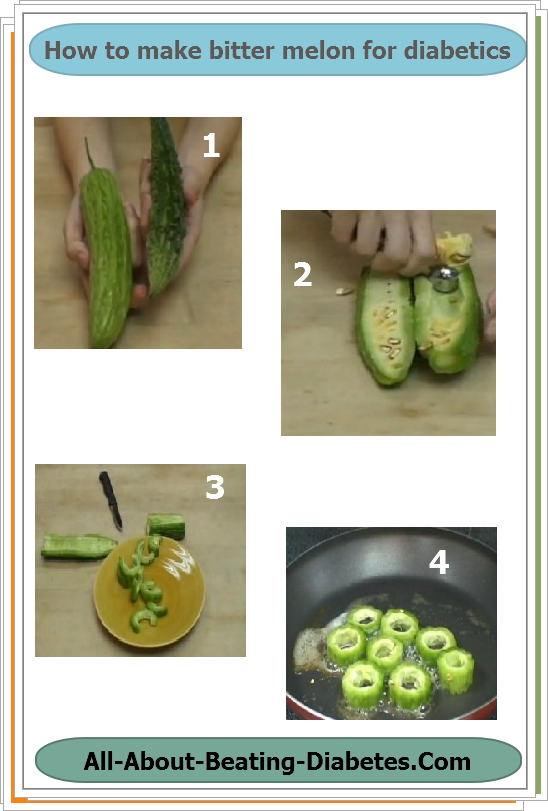
Simple recipe of cooking bitter melon as following:
|
Step no. 1: Take your favorite bitter melon fruit. They come to various types: small, bigger, slimmy, fatty, etc. I have seen that in South-East Asia, they prefer mostly small and near-slimmy bitter gourd fruits like the one shown on the right. |
|
Step no. 4: Then you can cook: I have seen that in South-Asia, they usually fry bitter gourd as shown in the picture on the right. Unfortunately, although bitter melon would come better in taste, it would not be a healthy-cooked food. The best choice could be steaming or boiling or just prepare some bitter melon salads mixed with other fruits or vegetables. |
At the end, "Buon appetite!". I have tasted, and looks really bitter.
I admit I do not eat it randomly, but when in my staying in South-East Asia, I have tasted several times, especially steamed, and sparkled with lemon juice and mixed with white salad:))
Are there any side effects or risks associated with consuming bitter melon for diabetes?
While bitter melon is generally considered safe for most people when consumed in moderate amounts, there are some potential side effects and risks associated with its consumption, especially for individuals with certain conditions or those taking specific medications.
Here are some considerations:
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Bitter melon has blood sugar-lowering properties, and if combined with other medications or natural supplements that have the same effect, it could lead to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Individuals with diabetes or those taking medications to lower blood sugar levels should monitor their blood glucose levels closely when incorporating bitter melon into their diet.
- Gastrointestinal Effects: Bitter melon can cause digestive discomfort, including abdominal pain and diarrhea, especially when consumed in excessive amounts. It's advisable to start with small quantities to assess your tolerance.
- Allergic Reactions: Some people may be allergic to bitter melon. Allergic reactions could manifest as itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. If you experience any of these symptoms, discontinue use and seek medical attention.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Pregnant and breastfeeding women should exercise caution with bitter melon consumption. It may stimulate menstruation and could potentially cause complications during pregnancy
- Interactions with Medications: Bitter melon may interact with certain medications, including those prescribed for diabetes.
It can enhance the effects of medications that lower blood sugar, leading to hypoglycemia. If you are taking medications, consult with your healthcare provider before adding bitter melon to your diet.
- Kidney Issues: Bitter melon contains compounds that could potentially worsen kidney problems. Individuals with kidney issues should consult their healthcare provider before consuming bitter melon.
- Low Blood Pressure: Bitter melon may have hypotensive (blood pressure-lowering) effects.
Individuals with low blood pressure should monitor their blood pressure closely and consult with their healthcare provider before consuming bitter melon.
Can bitter melon be used as a substitute for diabetes medication?
This is a complex answer and should think it over carefully. It is true bitter melon can have sugar lowering effect. However, we do not recommend to use as a substitute for diabetes medication.
Once your blood sugar is going down, you should adjust the dosage of your medications. This is true. But, should not use it as substitute to your medications unless your blood sugar is getting near normal or acceptable levels for several months without spiking.
Are there any scientific studies supporting the use of bitter melon for diabetes?
Yes, there have been scientific studies exploring the potential effects of bitter melon on diabetes.
However, it's important to note that the evidence is not always consistent, and more research is needed to establish the efficacy, optimal dosage, and long-term effects.
Here are some key findings from selected studies; I'm presenting only a few of them. You can use as reference:
1. Randomized Controlled Trial of Momordica charantia for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus:
Reference: Ooi CP, Yassin Z, Hamid TA. "Momordica charantia for type 2 diabetes mellitus." Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Aug 15;8:CD007845. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007845.pub3.
Summary: This Cochrane review analyzed the available randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on the use of bitter melon for type 2 diabetes. The review concluded that there was limited evidence supporting the use of bitter melon for improving glycemic control.
2. Hypoglycemic effect of bitter melon compared with metformin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients: A randomized control trial:
Reference: Miura T, Itoh C. "Hypoglycemic effect of bitter melon compared with metformin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients." J Ethnopharmacol. 2004 Sep;93(2-3):369-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.04.023.
Summary: This study compared the hypoglycemic effect of bitter melon with metformin in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes patients. Bitter melon showed a significant hypoglycemic effect, but the authors recommended further research.
3. Effect of Momordica charantia on the glucose tolerance in maturity onset diabetes:
Reference: Srivastava Y, Venkatakrishna-Bhatt H, Verma Y, Venkaiah K, Raval BH. "Antidiabetic and adaptogenic properties of Momordica charantia extract: An experimental and clinical evaluation." Phytother Res. 1993 Nov;7(7):285-9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2650070406.
Summary: This study investigated the effect of bitter melon on glucose tolerance in individuals with maturity onset diabetes. The results suggested an improvement in glucose tolerance.
4. Charantin:
Reference: Leatherdale BA, Panesar RK, Singh G, Atkins TW, Bailey CJ. "Improvement in glucose tolerance due to Momordica charantia (karela)." BMJ. 1981 Jul 11;283(6284):109-12. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6284.109.
Summary: This study investigated the hypoglycemic effects of bitter melon, with a focus on charantin. The results suggested an improvement in glucose tolerance.
5. Vicine and Polypeptide-p:
Reference: Dans AM, Villarruz MV, Jimeno CA, Javelosa MA, Chua J, Bautista R, Velez GG. "The effect of Momordica charantia capsule preparation on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus needs further studies." J Clin Epidemiol. 2007 Jun;60(6):554-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2006.07.009.
Summary: This study explored the effects of a Momordica charantia capsule preparation, including its potential impact on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. Polypeptide-p is mentioned as one of the components.
6. Momordicosides:
Reference: Chen Q, Chan LL, Li ET. "Bitter melon (Momordica charantia) reduces adiposity, lowers serum insulin and normalizes glucose tolerance in rats fed a high-fat diet." J Nutr. 2003 Jun;133(6):1088-93. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.6.1088.
Summary: This study investigated the effects of bitter melon on adiposity, insulin levels, and glucose tolerance in rats. Momordicosides are mentioned in the context of the plant's effects.
|
Written by Dr.Albana Greca Sejdini, Md, MMedSc Medically reviewed by Dr.Ruden Cakoni, MD, Endocrinologist |
Last reviewed 11/10/2023 |
Explore more herbs.
Diabetes complications Questions or Problems? Get Help Here
This is the place where you can ask a question about any aspect of diabetes complications.
It's free and it's easy to do. Just fill in the form below, then click on "Submit Your Question".