Diabetes Kidney Disease
- Home
- Complications
- Diabetes Kidney Disease Pathogenesis and Prevention
Developing kidney disease is one of the worst complications related to diabetes, and one of the top reasons for fatalities in people who suffer from diabetes. Nephropathy happens approximate 15 years after the doctors have diagnosed diabetes.
Pathophysiology - How and Why does the disease progress?
The pathophysiology of diabetic kidney disease (nephropathy) is related to the microangiopathy, which is a condition where the small blood vessels are damaged. This has a great impact on the kidney.
The main role of the kidney is to filter and purify the blood in the organism. Moreover, it has really important role in removing the excess water in our body. If these functions fail, then the symptoms are predictable to happen.
There is one part of the kidney, which is extremely hard. This part is called glomerulus and it is one of the most important parts of the kidney because, without it, our blood will not be able to be cleaned out of the toxic and waste products of our cells.
In the state of nephropathy in diabetics, there is thickening of the glomerulus and it is not able to function properly.
One of the first symptoms, which can be detected by the doctors, is the increased amount of albumin, which is a protein commonly found in the blood, in the urine.
Usually, there is no protein of any kind in the urine. The presence of such proteins means that the glomerulus apparatus is damaged.
As the nephropathy progresses, more glomerulus will be destroyed or damaged by the sclerosis (the thickening process).
The kidney disease in diabetics has other problems, too. One of the most important things about the kidney is the possibility of secretion of the hormone called erythropoietin.
This hormone is responsible for increasing the amount of red blood cells in our body. The impaired kidney no longer produces this hormone and therefore, there is decrease in the amount of red blood cells.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms
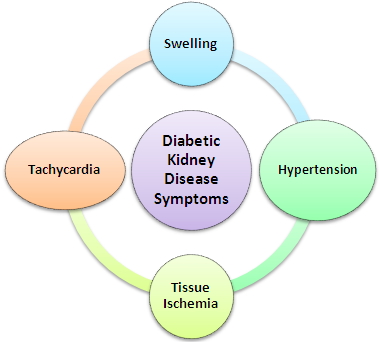
The symptoms and problems could be summarized:
1. Increased blood volume
1. Swelling - under the eyes, especially in the morning
2. Developing hypertension:
a. headache
b. vomiting
c. nausea
d. tachycardia
3. Low quantity of red blood cells
a. Adynamia (you do not want to move or do any work)
b. Increased heart rhythm (the tachycardia)
c. Tissue ischemia ( places where the blood is insufficient)
These are the main symptoms and problems, however, there exist some others, that contribute further to worsening the patient’s condition.
There are many symptoms that could be noted by the patients. Swelling is the first thing that they can see with their own eyes. The swellings are usually in the upper part of the body, especially around the eyes.The specific time for them to appear is after a night sleep. If you notice this, go to your doctor.
Hiccups are also very common in diabetes nephropathy. Fatigue is another symptom commonly noted, but it is not specific to the disease.
Arterial hypertension (hypertensive nephropathy), because the blood could not be filtered, due to destroyed glomerulus, is the symptom that patients can not see but they will feel.
Headache is the symptom that is in direct correlation with the increase of arterial pressure.
Moreover, because of this, you will feel vomiting or nausea. These symptoms lead to an increase arterial pressure. If your doctor notices such symptoms, and he/she knows that you have diabetes, he/she will ask to run a kidney biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. If confirmed, immediate treatment is advised to start.
Treatment of diabetes kidney diseases
The treatment is extremely hard. If one of the kidneys is not damaged, this is good and the prognosis is going to be better for the patient. However, if both of the kidneys are impaired, the prognosis is not that good.
- Following the right diet is one of the main points in the therapy of kidney impaired by diabetes. You have to keep your glucose level in certain boundaries. If you do this, you will be able to slow down the progress of your kidney’s destruction. Diet must be modified to better to the patient’s need. However, there has to be a strict control of the glucose level, as well as the serum creatinin. Protein intake also has to be modified in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
- Using vasodilators as medications to better you kidney blood flow is a good as a starting therapy. There are many drugs that have this kind of effect, including ACE inhibitors (Sartans) and some kinds of drugs made by herbs.
The weapon of first choice is the group of medicaments known as ACE inhibitors. They stop the very important metabolic chain, which contributes to the increase in arterial blood pressure.
In additon, ACE inhibitors have positive effect on the kidney, slowing down the progression of the disease. These drugs reduce hypertension too.
Unfortunately, in most cases, diabetic kidney disease leads to development of chronic renal failure, where the kidney is no longer able to do its work.
In this case, dialysis is the only thing that can help.
However, this is just a temporary solution and because of the bad damage to your kidneys, the renal
(kidney) transplant is the only thing/solution that can save your life.
Does having only one kidney give false diabetes reading?
You have to know that the blood glucose concentration depends on the amount of glucose acquired with the food and the amount of glucose used during the day.
So, there are two possible factors to cause high blood glucose level:
1. higher intake of glucose and
2. low glucose usage.
Kidney is made up to excrete the excessive glucose when its blood concentration is higher than normal. Therefore, the role that kidney plays is shown only if blood glucose is higher than normal.
Other thing, which you have to know, is that having one kidney is not messing up the blood glucose result at all. Because of this, the kidney is not responsible for false positive or false negative results.
However, it is important for you to know that, if you have only one kidney, the risk for chronic renal failure, caused by inadequate control of the blood glucose concentration, is higher.
So, my advice for you is to do everything possible in purpose to keep your blood glucose level with in the normal ranges, which are 64.8-104.4mg/dl or 3.5-6.1mmol/l, depending on the unit of measurement.
To put it differently, you have to follow low carb diet, doing exercises, taking your medications regularly and to check your blood glucose level every day.
Written by Dr.Albana Greca Sejdini, Md, MMedSc
Medically reviewed by Dr.Ruden Cakoni, MD, Endocrinologist
Last reviewed 07/29/2021
References:
Diabetes complications Questions or Problems? Get Help Here
This is the place where you can ask a question about any aspect of diabetes complications.
It's free and it's easy to do. Just fill in the form below, then click on "Submit Your Question".