Gestational Diabetes Test
- Home
- blood sugar levels
- Gestational Diabetes Test
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and usually goes away after delivery. To diagnose gestational diabetes, a glucose screening test is typically done between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
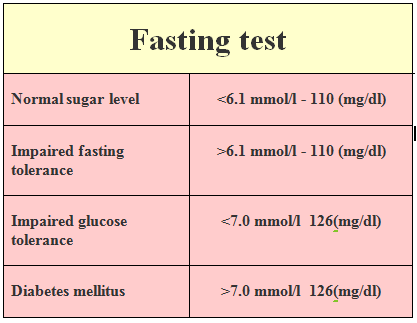
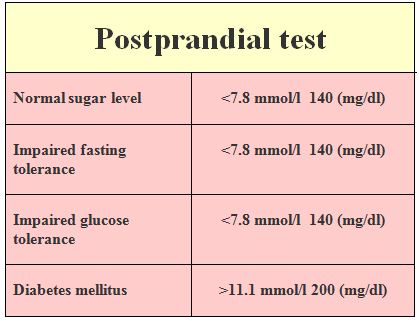
To interpret the results of gestational diabetes tests, it is important to understand the normal range of glucose levels in the body, which typically falls between 3.6 and 5.8 mMol (65-105 mg/dl).
There are various types of gestational diabetes tests available, including non-challenging tests and screening glucose challenge tests.
1. Non- challenging tests
- include fasting glucose tests, postprandial tests, and random glucose tests, which can be performed during pregnancy to diagnose gestational diabetes without requiring glucose or food intake.
a. Fasting glucose tests
- these are the most popular test used by almost all doctors who are dealing with endocrine diseases. It is done early in the morning after fasting for 8 hours.
b. Postprandial test,
which means that you will be tested 2 hours after your meal. You have to be very strict about that otherwise the test will not be working. This is the second best gestational diabetes test.
c. Random glucose test
This test will be performed three times during the day. Each time blood will be taken and the glucose level will be measured.
It is called random because you will be tested several times during the day in different time intervals, before, after and during your meals. It could be carried out during pregnancy and it is able to diagnose gestational diabetes.
2. Screening glucose challenge test
The screening glucose challenge test, conducted between 24-28 weeks of pregnancy, involves drinking a water solution with 50 grams of glucose and having blood drawn one hour later to determine sugar levels.
However, this test is not always effective, and an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) may be recommended to diagnose gestational diabetes.
3. Oral glucose tolerance test
The OGTT involves a strict protocol, where the patient is allowed to eat normally for three days without restrictions on movement.
On the day of the test, the patient consumes at least 150 grams of carbohydrates and drinks a glucose solution while blood glucose levels are measured at specific intervals.
After that the patient has to visit the doctor and there she will be given a solution of glucose.
She has to drink it and then the blood glucose level will be measured on certain intervals. This is the best gestational diabetes test, which could be carried out through the pregnancy to find the disease.
What if I find high blood sugar levels during pregnancy?
If your blood sugar levels are higher than normal during the screening or glucose tolerance test, your doctor may diagnose you with gestational diabetes.
Treatment for gestational diabetes typically involves making dietary changes and increasing physical activity. In some cases, medication may also be necessary.
Gestational diabetes test is something that each mother has to undergo, when she is about to have her baby. About 10% of all mothers develop this kind of condition, while they are pregnant.
That’s why finding this disease really fast will help the doctors treat the mother better and more effective.
|
Written by Dr.Albana Greca Sejdini, Md, MMedSc Medically reviewed by Dr.Ruden Cakoni, MD, Endocrinologist |
Last reviewed 03/11/2023 |
References:
References:
- American Diabetes Association. (2021). 14. Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care, 44(Supplement 1), S200-S210. doi: 10.2337/dc21-S014
- International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups Consensus Panel, Metzger, B. E., Gabbe, S. G., Persson, B., Buchanan, T. A., Catalano, P. A., . . . Trimble, E. R. (2010). International association of diabetes and pregnancy study groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes care, 33(3), 676-682. doi: 10.2337/dc09-1848
- Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. (2018). Practice Bulletin No. 190: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 131(2), e49-e64. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000002501
Diabetes complications Questions or Problems? Get Help Here
This is the place where you can ask a question about any aspect of diabetes complications.
It's free and it's easy to do. Just fill in the form below, then click on "Submit Your Question".