Causes of Metformin Weight Loss Problems!
- Home
- Your Diabetic Information Center
- Metformin Weight Loss
Metformin is a medication commonly prescribed to manage type 2 diabetes. While it is effective in controlling blood sugar levels, one of its side effects is weight loss.
However, some people may experience difficulties with metformin-induced weight loss, and there can be several possible reasons for this:

- Dosage: If the dosage of metformin is too high, it can cause excessive weight loss. In such cases, the dosage may need to be adjusted by a doctor.
- Dietary changes: Some people may not adjust their diet when starting metformin, which can lead to weight loss. It's important to maintain a healthy, balanced diet while taking metformin.
- Underlying conditions: People with conditions such as an eating disorder, thyroid problems, or other hormonal imbalances may have difficulty with metformin-induced weight loss.
- Medication interactions: Metformin may interact with other medications that affect weight, such as antidepressants or antipsychotics, leading to weight gain or loss.
- Individual differences: Some people may simply be more susceptible to the weight loss side effect of metformin than others.
Metformin Weight Loss Link -
Overweight and insulin
Metformin is known to promote weight loss in overweight non-diabetic patients by targeting insulin levels. Within a few weeks of starting this drug therapy, patients can experience significant weight loss.
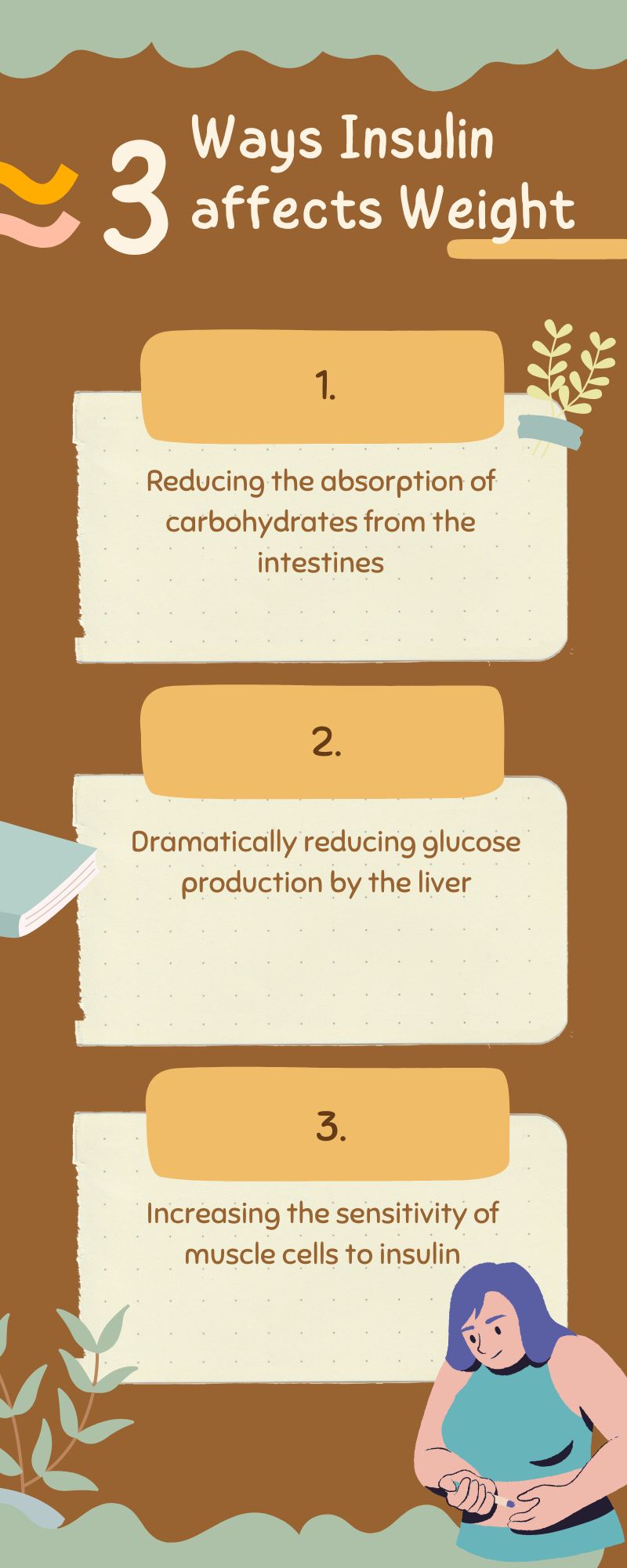
While metformin is primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes, it is also prescribed in weight loss programs due to its effectiveness. The drug influences weight through three main mechanisms:
- Reducing the absorption of carbohydrates from the intestines
- Dramatically reducing glucose production by the liver
- Increasing the sensitivity of muscle cells to insulin, which is the most important and notable effect of metformin.
Metformin Weight Loss - Why is insulin so important for overweight people?
The relationship between insulin and weight gain is straightforward: the greater the insulin level in your body, the more likely you are to gain weight.
When you consume food, particularly sweet items, your blood sugar rises, which prompts your pancreas to release insulin.
If you continue to eat, your pancreas produces more insulin. Additionally, insulin stimulates your brain, causing you to feel hungry.
This cycle of increased food intake and insulin production leads to greater hunger and weight gain.
If your cells are sensitive to insulin, however, you will not have difficulty gaining weight because your cells will utilize glucose efficiently, breaking the vicious cycle.
Metformin is a medication that is frequently prescribed to overweight individuals who have trouble losing weight due to insulin resistance.
It functions by decreasing the amount of glucose generated by the liver and enhancing the body's sensitivity to insulin, allowing cells to utilize glucose more efficiently.
This results in lower insulin levels, less hunger, and consequently, weight reduction.
Metformin Weight Loss Cure
Rapid improvement can be observed in patients who start taking Metformin for weight loss. This is because the medication reduces the liver's production of glucose, which in turn reduces insulin secretion. As a result, there is no substance to trigger hunger, leading to reduced food intake and subsequent weight loss.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common cause of weight gain in women, often due to elevated insulin levels in the bloodstream. Metformin can also be used to assist these women in managing their condition and achieving weight loss goals.
Metformin Weight Loss - How to decide whether this is the right drug for you?
If you are considering using Metformin as a weight loss treatment, it is essential to have your BMI checked by a healthcare provider. If your BMI exceeds the maximum value of 25, your doctor may prescribe Metformin.
Another reason for starting this treatment is if you have elevated blood sugar levels or have been diagnosed with diabetes.
It is critical to remember not to increase your dose without consulting a medical professional, as doing so may result in unwanted side effects.
Athletes are advised against using this drug as it may cause hypoglycemia, which can be dangerous for them. This is because Metformin can significantly reduce blood glucose levels, which, combined with the effects of intense physical activity, can be harmful.
|
Written by Dr.Albana Greca Sejdini, Md, MMedSc Medically reviewed by Dr.Ruden Cakoni, MD, Endocrinologist |
Last review 4/27/2023 |
References:
References:
- Rena, G., Hardie, D. G., & Pearson, E. R. (2017). The mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia, 60(9), 1577-1585.
- DeFronzo, R. A., & Goodman, A. M. (1995). Efficacy of metformin in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine, 333(9), 541-549.
- Zhou, G., Myers, R., Li, Y., Chen, Y., Shen, X., Fenyk-Melody, J., ... & Yang, W. (2001). Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 108(8), 1167-1174.
- Derosa, G., & Maffioli, P. (2019). The role of a fixed combination of lorcaserin and metformin in the management of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review. Diabetes Therapy, 10(2), 441-452.
- Apovian, C. M., Aronne, L. J., Bessesen, D. H., McDonnell, M. E., Murad, M. H., Pagotto, U., ... & Still, C. D. (2015). Pharmacological management of obesity: an endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 100(2), 342-362.
- Seifarth C, Schehler B, Schneider HJ. Effectiveness of metformin on weight loss in non-diabetic individuals with obesity. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2013 Jan;121(1):27-31. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1327734. Epub 2012 Nov 12. PMID: 23147210.
Diabetes complications Questions or Problems? Get Help Here
This is the place where you can ask a question about any aspect of diabetes complications.
It's free and it's easy to do. Just fill in the form below, then click on "Submit Your Question".